Subnetting in a nutshell is a logical division of an IP network. It is done to provide a better network management, for security purposes or to simplify the network topology. This is necessary for system administrators, network engineers, database administrators and so on.
Understanding how to subnet is a detailed topic. Here are a few excellent resources to start with :
Basically, to understand subnetting, we need to look at two basic things  : the IP address and the subnet mask.
Also, there is something known as CIDR notation that indicates what is a given subnet for a network. Example : for a given network, if the CIDR notation is 192.168.10.1 / 24, what this means is that the first 24 bits are reserved for the network component and last 8 bits are for host component. The total of both will always be 32 bits. The same notation can be displayed as : 192.168.10.1 and 255.255.255.0 (192.168.10.1 being the network and 255.255.255.0 being the subnet mask).
Gip is a useful subnet calculator available for Ubuntu/Linux Mint. It will quickly provide all the required details regarding subnets.
To install it, open Terminal and type :
Once installed, it will show up in Accessories menu or search for it from the Unity dashboard (Ubuntu).
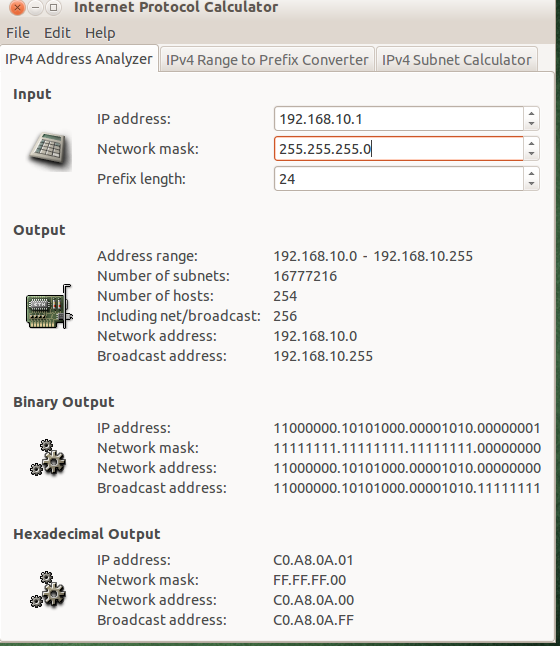
Gip using the “IPv4 Address Analyzer” will display various subnet details like address range, number of networks, number of hosts, the network address, the broadacast address and also their binary equivalent.
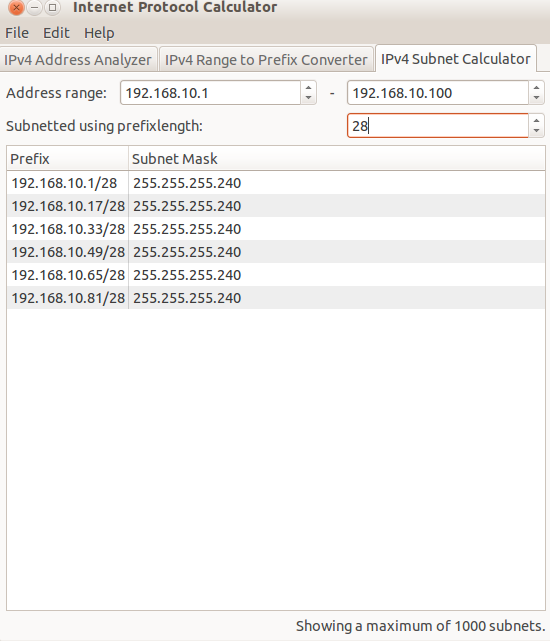
To subnet using Gip, from the Ipv4 Subnet calculator, enter the address range and the subnet mask (24 is 255.255.255.0, or say 28 which is 255.255.255.240). It will display the subnetted networks based on that.
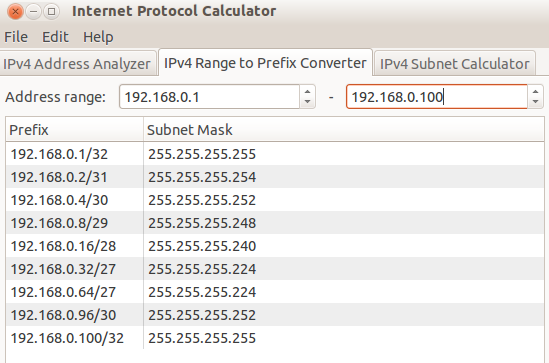
Also, for a given network range, it will break down the prefix with the subnet mask as shown below :
This is a lightweight tool that can make subnet calculations easy.
Happy subnetting!
