Bash shell has a robust history feature which makes it easy to keep a track of previous commands that can be run again whenever needed.
So if you spend a lot of time with Linux commands, this can save time by not entering same commands over and over.
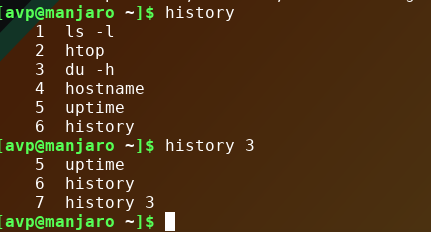
Seeing previously used commands:
To get a list of previously used commands, from the shell/Terminal type:
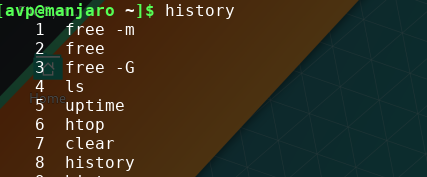
This will show all the commands as a list. The numbers make it easy to run them again without typing.
Run previous commands from history:
So to run the 5th command from the list above, specify that number :

To execute the previous/last typed command, use:
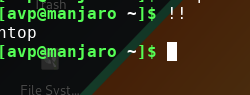
Also, if you first want to know what the last command really was rather than directly running it:
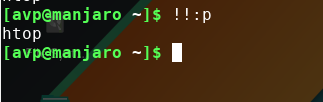
The difference between !! and !!:p is that while the former directly runs the last command, the latter simply echoes it in Terminal and doesn’t run it.
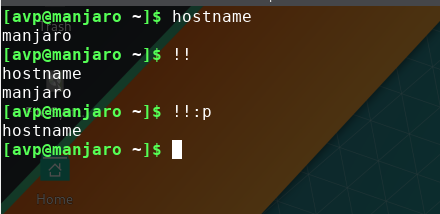
You can also quickly list the last few commands, so to know which were the previous 3 commands, use :
Use shell scripts or aliases for long commands:
To avoid typing really long commands or multiple ones, just put them in a shell script and run that whenever needed. Another option is to set a short alias for them.
If it were the last command that is needed, redirect by typing :
echo “!!” >> diskuseuptime.sh
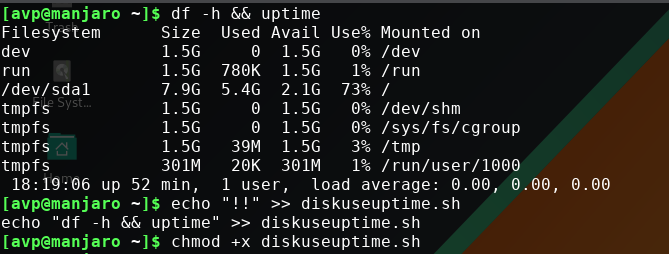
As with all shell scripts, first make it executable and then run it.
./diskuseuptime.sh
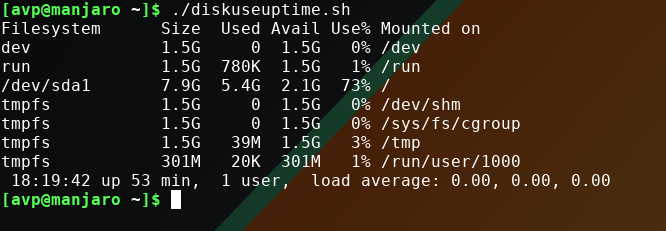
The output will be the same as the commands entered before.
Clearing the history list:
Finally, to clear the history list, use the -c option :
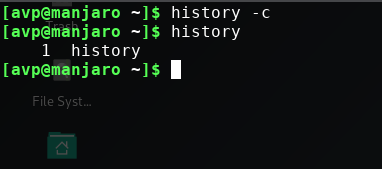
Overall, the history feature of Bash shell is a powerful option which can be a timesaver when frequently working with Linux command line.
All done.