Stacer is a system optimizer which can monitor system load, uninstall apps, tune-up system and manage processes. It has a cool graphical dashboard that makes it easy to monitor the system resources in use and also optimize them.
Here is how to install and use it for Linux Mint and Ubuntu:
First, add the required repository for installing it from the Terminal by typing:
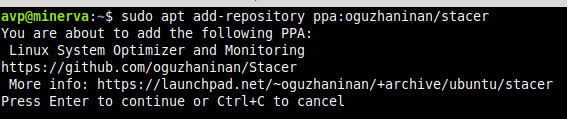
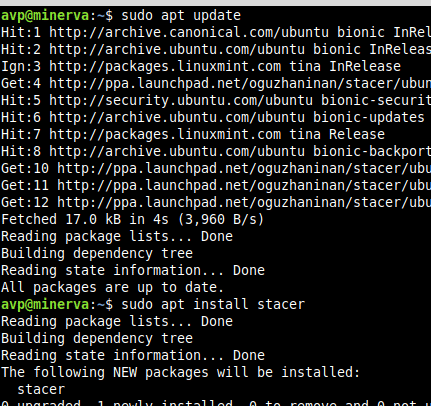
Next, update and install the tool:
sudo apt install stacer
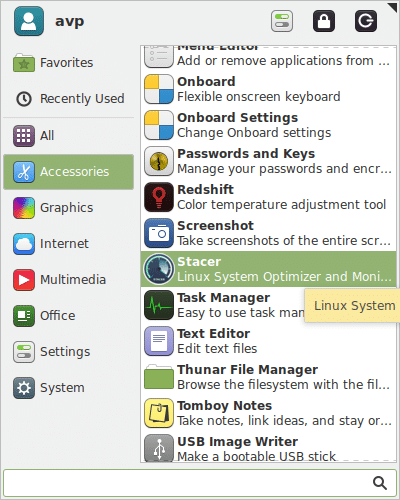
Once installed, it will show up in the system menu or you can search for it if it is installed in Ubuntu. (Accessories in this example that uses Linux Mint XFCE).
Stacer link has eleven components to it which make managing the system tasks easy. They can be accessed from the left column.
Dashboard: This is the default view and it has a cool view of the system details which shows CPU, memory and disk information.
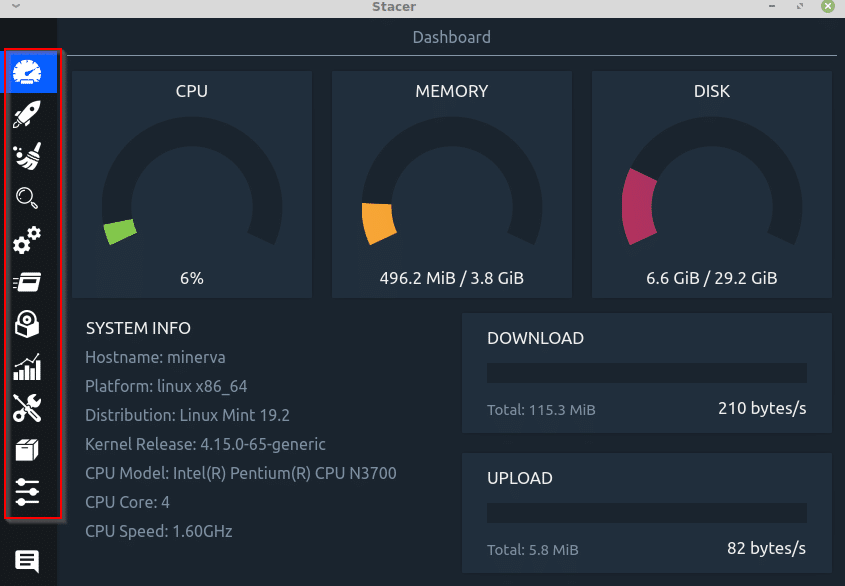
It is similar to Task Manager in Windows wherein you can get a quick system snapshot that can be useful for troubleshooting. You can also keep track of total download and upload count from here.
Startup Apps: You can directly add an app that can run on startup from here. Click on Add Startup App to do that.
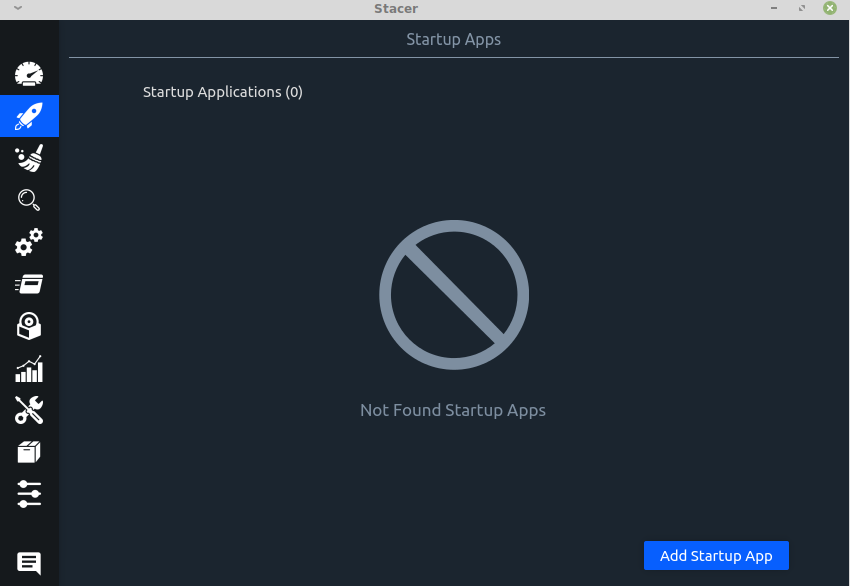
Also, if there are already existing apps that are enabled on startup, they will be listed here.
System Cleaner: Use this to remove cached files, empty trash as well as logs. Click on the search icon to search for the items to be removed.
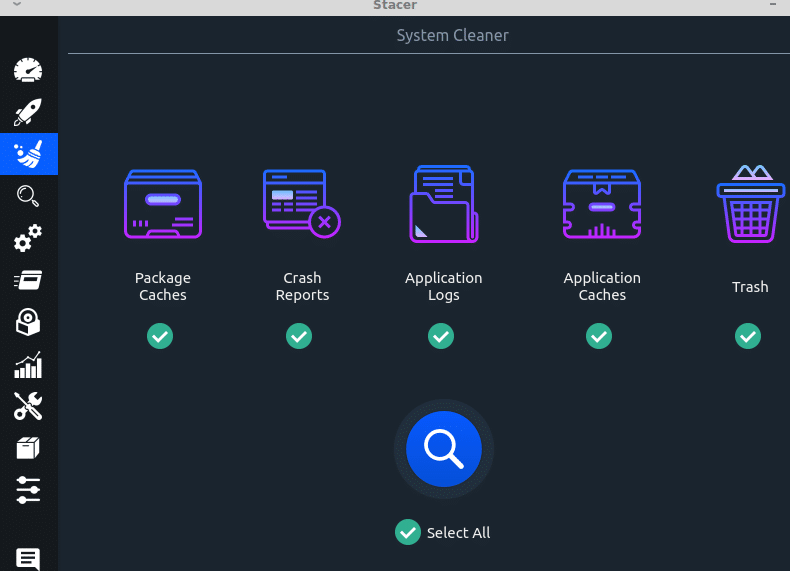
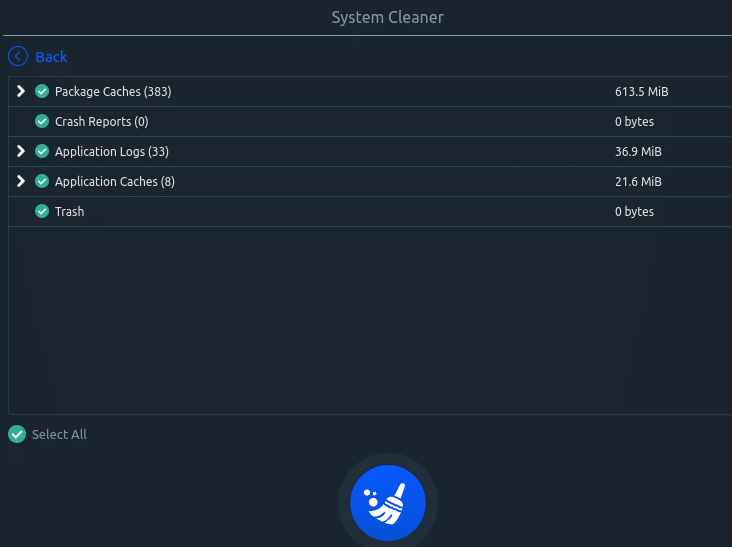
Then select them as needed and click on the brush icon to remove them.
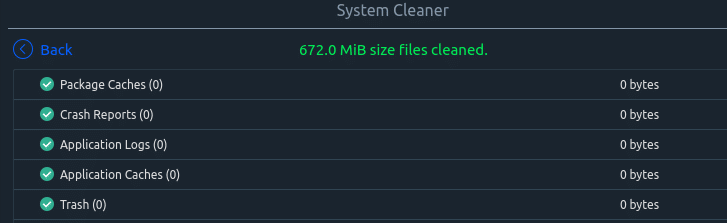
A quick summary of the total disk space freed and what was removed will be displayed after the cleanup is complete.
Search: Find files and folders with the search function.
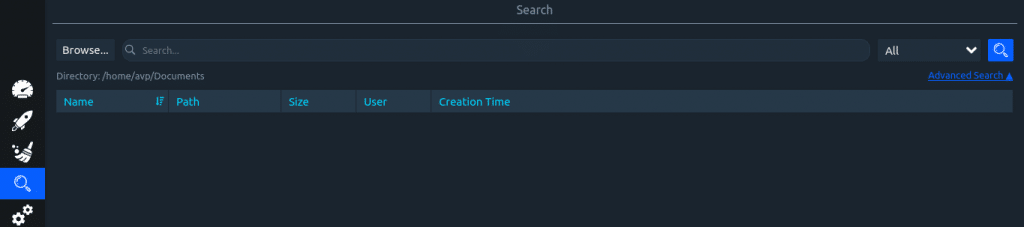
There is also an option of advanced search through which you can filter search criteria.
Services: A list of all the running services is displayed here by default.
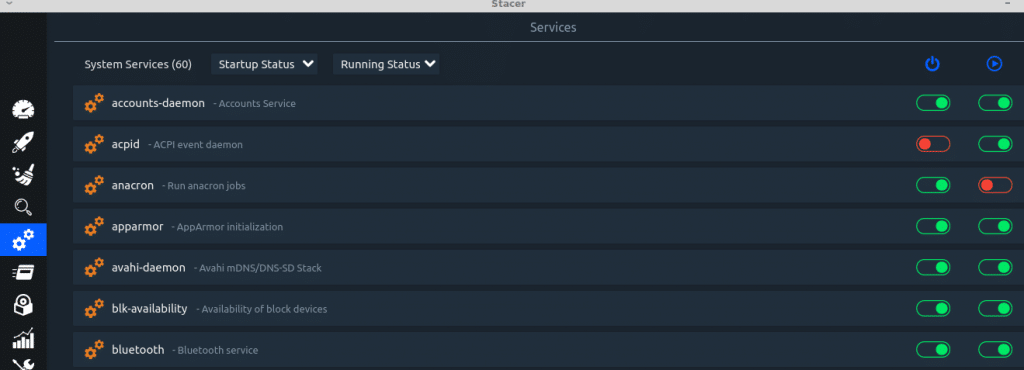
You can filter to view services that are not running as well which can be useful in troubleshooting.
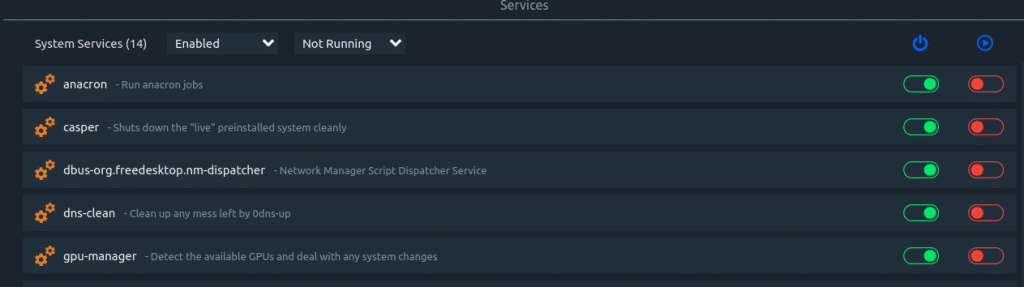
Turn individual services on or off using the slider.
Processes: Processes along with their system resources consumption and their PID (Process ID) are displayed here. This is similar to using htop to manage processes.
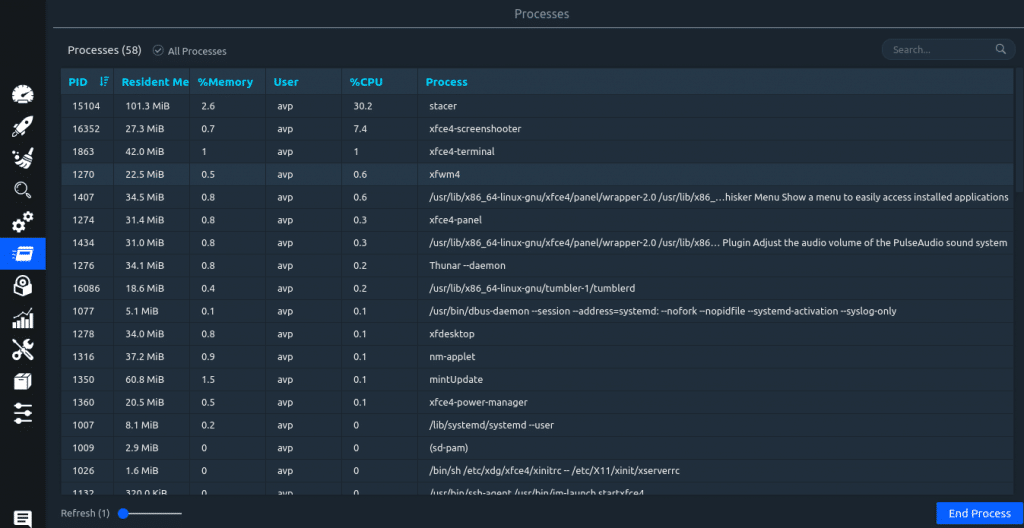
Click on the End Process button to stop any given process. Also, the refresh interval for the listing of processes can be changed from here.
Uninstaller: Uninstall packages with the Uninstaller. A list of installed packages will be listed.

You can also search for specific packages and then uninstall them by choosing Uninstall Selected.
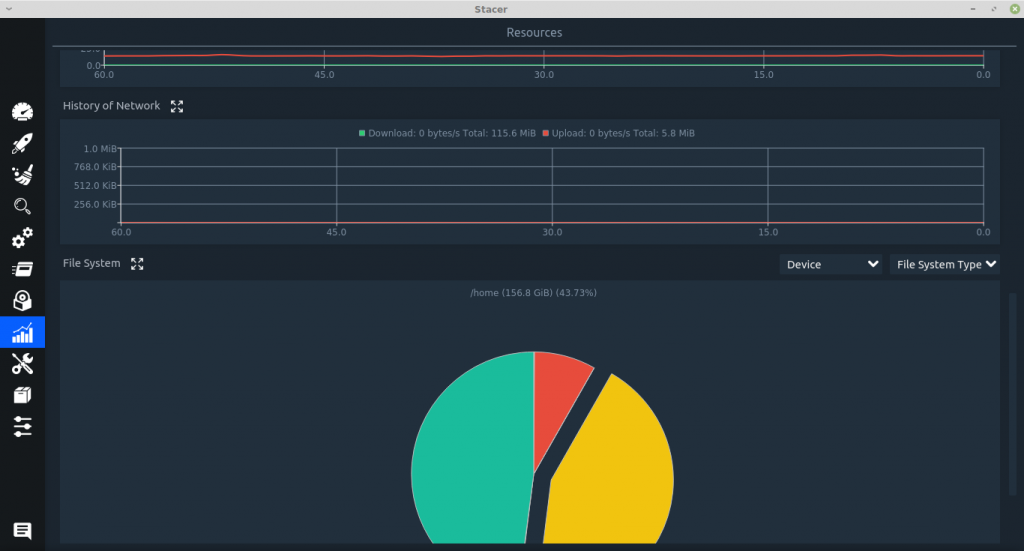
Resources: This gives a neat and detailed graphical view of CPU, memory, network and file system usage in the form of graphs and pie charts.

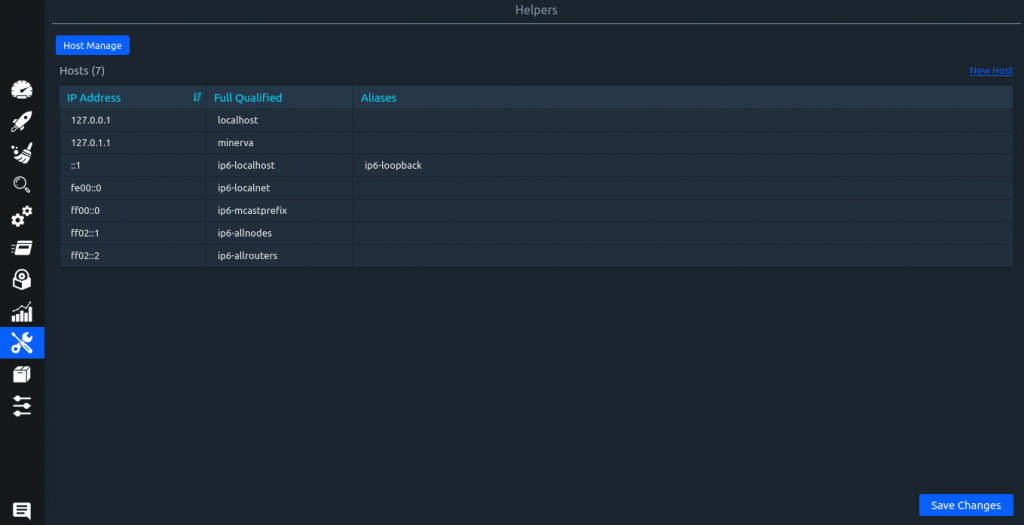
Helpers: Directly edit /etc/hosts file from here with Helpers. Add a new hostname and the corresponding IP address by clicking on New Host to update the hosts file from here.
APT Repository Manager: Change repository settings from here. Add new repositories by clicking Add Repository using this manager.
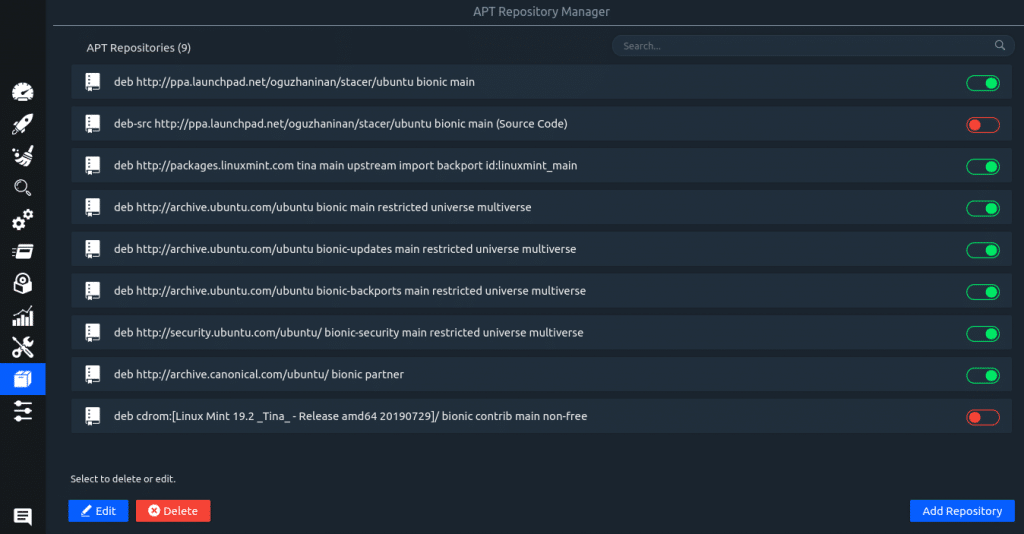
You can also disable a repository by turning off the corresponding slider.
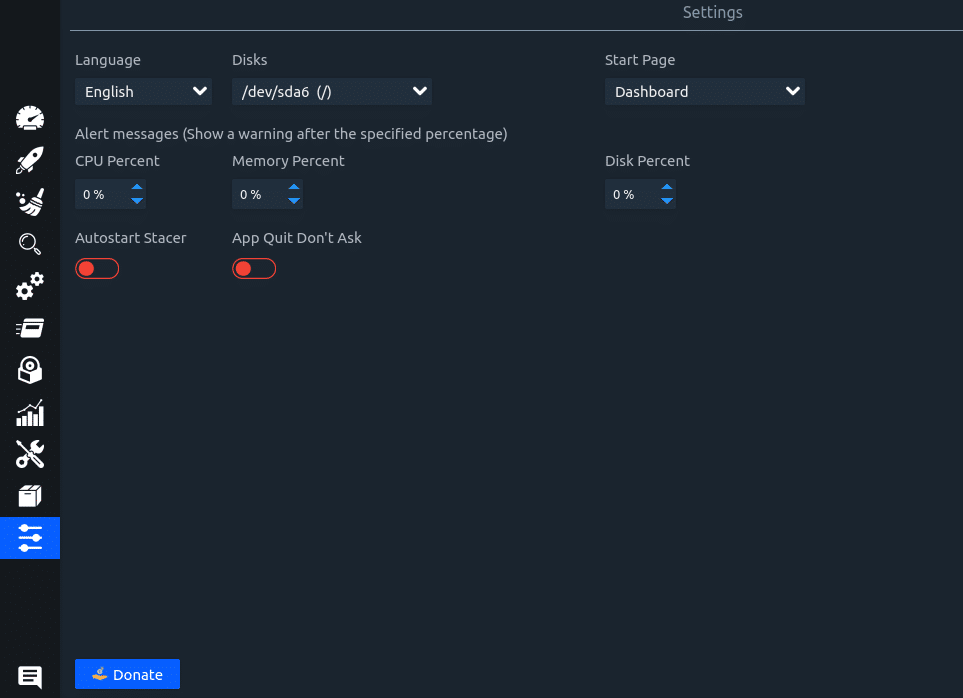
Settings: This is for configuring Stacer settings. Various options like changing the default view to be displayed (which is the Dashboard), directly exiting Stacer on close rather than it running in the background and adding alarms threshold for CPU, memory, and disk can be configured from here.
This is a cool and easy to use system optimization tool for Linux Mint and Ubuntu. Looks pretty awesome too.
All done.