If you’d like to spare some computing resources of your PC and help fight the COVID-19 pandemic, then you can do so using BOINC and Rosetta@home.
Rosetta@home or R@h is a not for profit project that researches and models protein structures that can ultimately help in fighting many major diseases besides COVID-19. But for doing that, it requires a huge amount of computing power which can be made possible by volunteers sparing their computing resources from all around the world. More details can be found on the project page with the latest updates.

BOINC (Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing) developed by the University of California, Berkeley is a volunteer grid computing software that can be used for various research projects. All you need to do is install it on the PC. It is non-intrusive, runs silently in the background and is available for all major platforms. (This example uses BOINC for Windows).
Download and install it from here. (The installer also offers a Virtual Box setup besides the standalone type if you would be running BOINC in a virtual machine) . This example uses a standalone installer.
During installation, you can continue to use its screensaver (default choice) or change these options by clicking on Advanced.
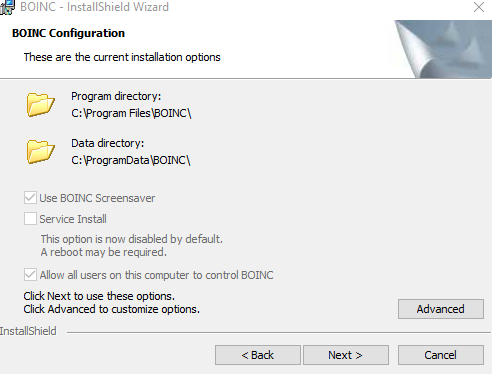
Also, if you’d like to turn off using your graphics resources, select Service Install. Click Next to complete the installation.
Reboot once prompted to do so.
After a reboot, launch BOINC. As it is a volunteer-based grid computing software, there will be many projects that you can contribute to.
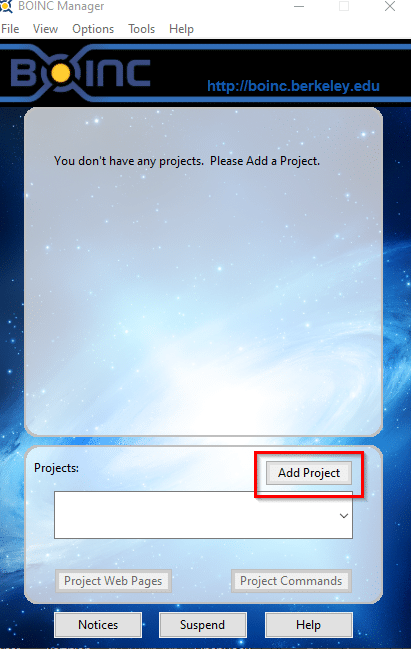
Click on Add Project. In this case, for COVID-19 select Rosetta@home.
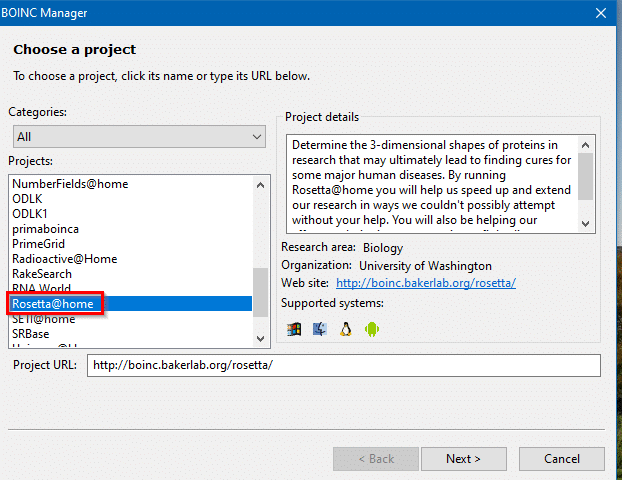
Create a Rosetta@home account by signing up.
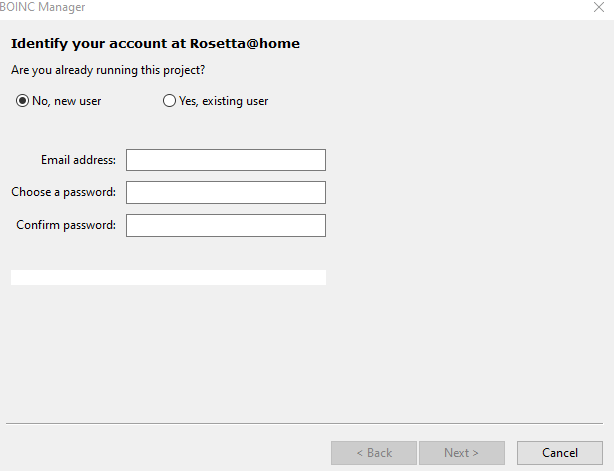
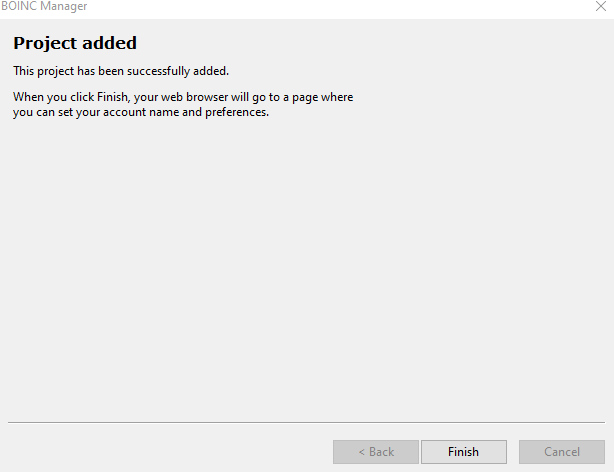
Once done, click Finish.
This will open a webpage that will ask you to enter a nickname along with some other details. Click OK.
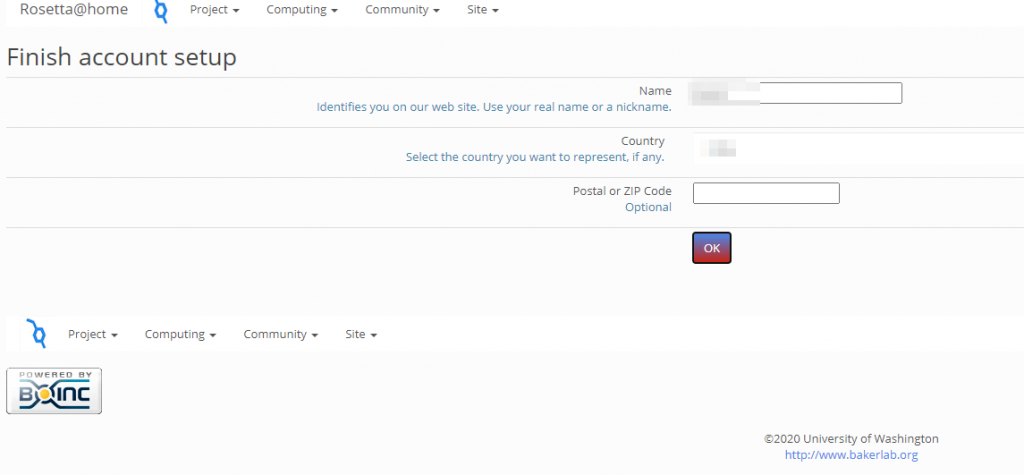
You can also join the Fold for Covid project team for this from here.
BOINC will now fetch the required tasks that are needed for Rosetta@home and start computing in the background.
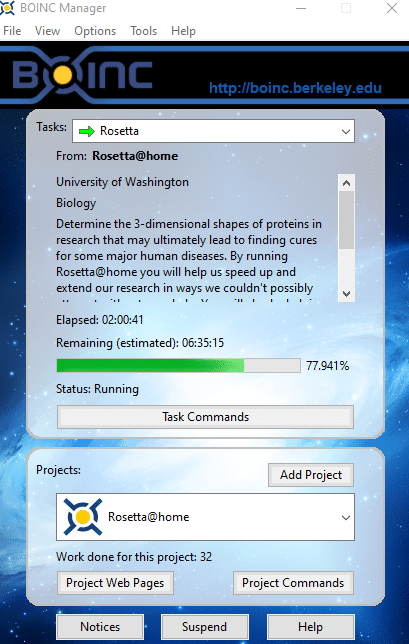
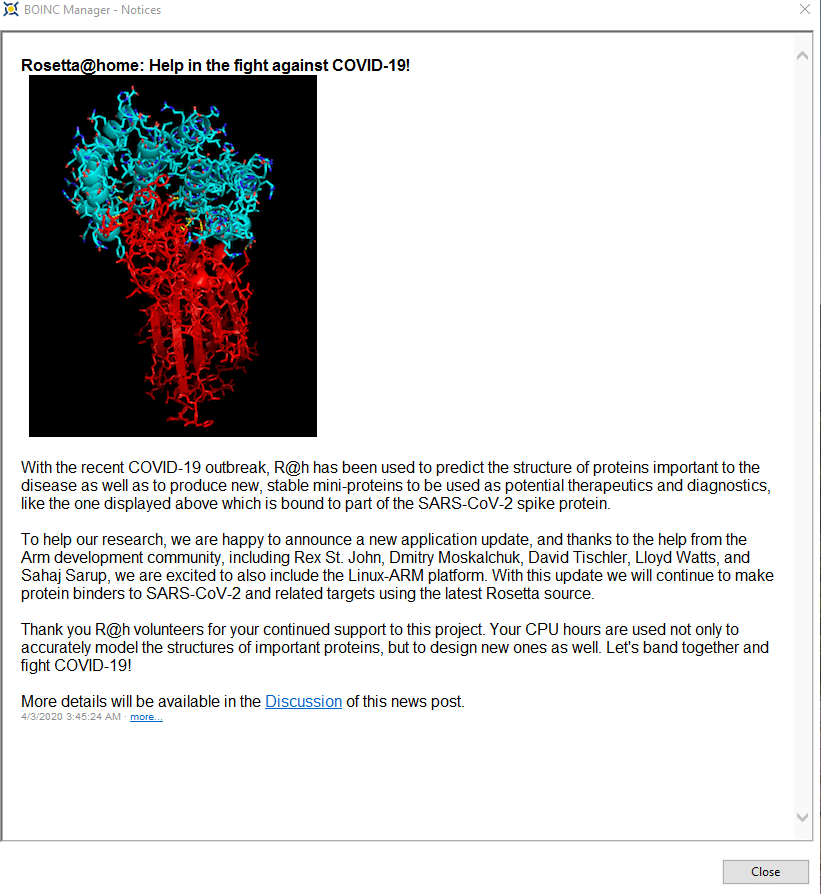
Click on the Notices button to get a brief background about this project.
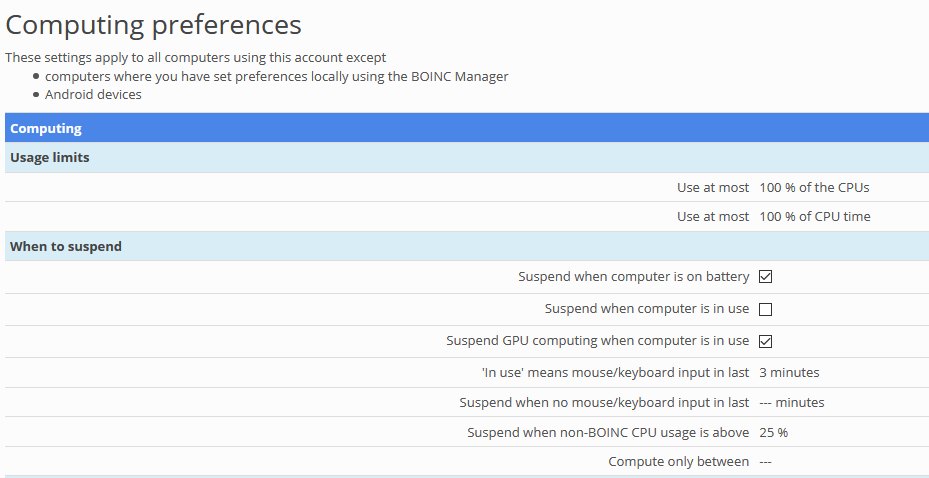
 If you’d like to limit the number of computing resources that need to be allocated for BOINC then click on Options > Computing preferences.
If you’d like to limit the number of computing resources that need to be allocated for BOINC then click on Options > Computing preferences.

From here you can set various limits and thresholds for CPU, disk space, and so on.
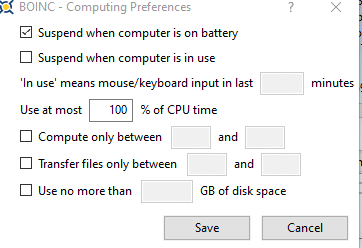
Also, if you’d like for BOINC to be active only during a set period, that too can be configured from here. To do that, enable the options for Transfer files and Compute only and set the start and end hours.
You can also change these preferences from your account settings by signing into the Rosetta@home webpage here.
The computing preferences changed from there will apply to all the devices (if you are using BOINC on more than one device) but they will be overridden if directly changed from the local device.
Various project-related updates can be directly accessed from BOINC by clicking on Project Web Pages.
You can also stop any computational activities by clicking on Suspend.
![]()
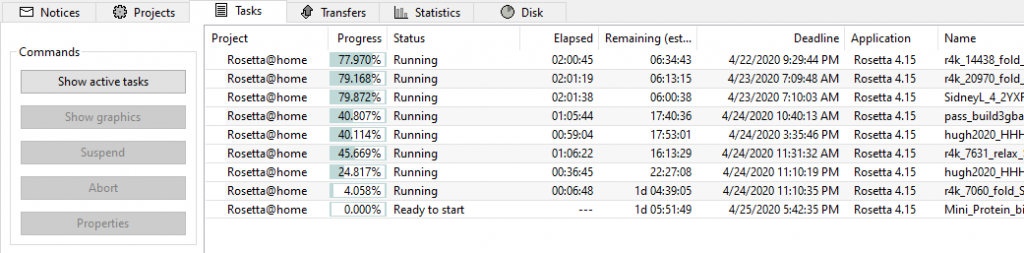
Also, to get an idea of how much computing resources BOINC is using, click on View > Advanced View.
![]()
This will show a detailed breakdown of the number of tasks that are running for Rosetta@home, the disk space and CPU utilization of your PC, and so on.
Also, if you have a spare PC available, you can directly install and use Balena OS for Rosetta@home. More details on that can be found here.
Happy computing and stay safe.
I have read your article, it was very helpful and helpful for me. I admire the valuable information you provide in your articles. The idea of using BOINC is very good while the COVID-19 pandemic is raging.