The history command in Linux is very useful for recalling previously typed commands.
When using it, you can also add a timestamp to the history’s list of previously used commands. This can be handy in knowing which commands were used when.
It is done by setting the HISTTIMEFORMAT Bash variable. Set it to display the date and time, and then history will show the timestamps next to the list of commands.
Here is how:
Open the Terminal and type in:
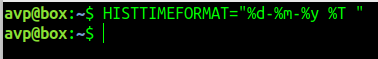
What this does is add a timestamp in the Day (%d)–Month(%m)–Year(%y) and Time(%T) format. The extra space after the Time(%T) parameter is so that the output doesn’t get too crowded.
Now run the history command. The list of commands will show the timestamp next to them.
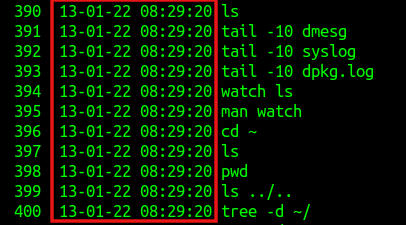
An important caveat when using HISTTIMEFORMAT is that it will not show the actual timestamps of previous commands, but will do so for all the subsequent ones from the date it was enabled.
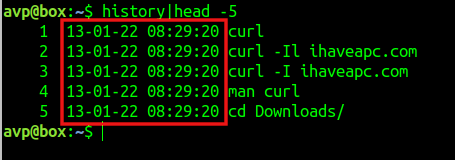
Different ways to display the history timestamp:
You can also rearrange the Day–Month–Year values as you like, so the timestamp format can also be set as:
This will show the timestamp in Month–Day–Year format.
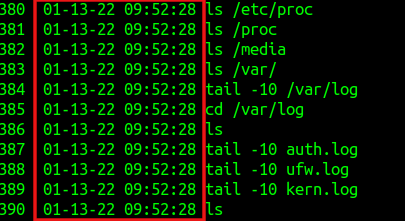
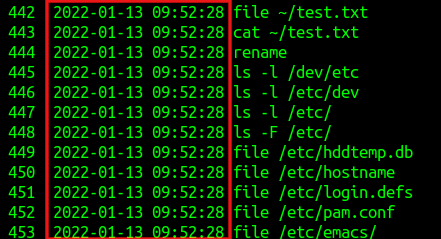
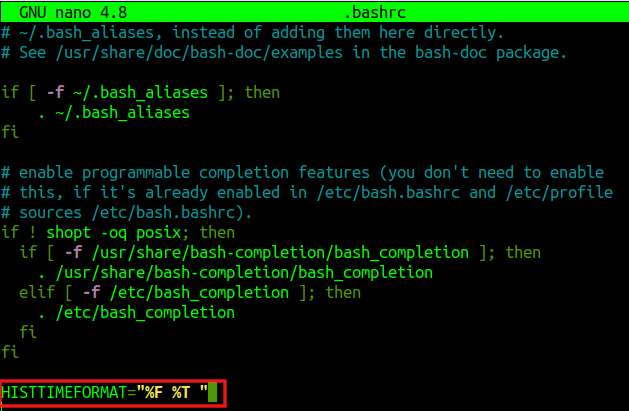
The %F parameter is for displaying the timestamp in the Year–Month–Day format.
Making the changes as persistent:
Setting this variable by default will only show the timestamp for the history command in the current session. So, just like other modifications (e.g: aliases), you can set HISTTIMEFORMAT as a persistent setting by editing the .bashrc file.
Open any text editor like vi or nano to open the .bashrc file from the home directory:
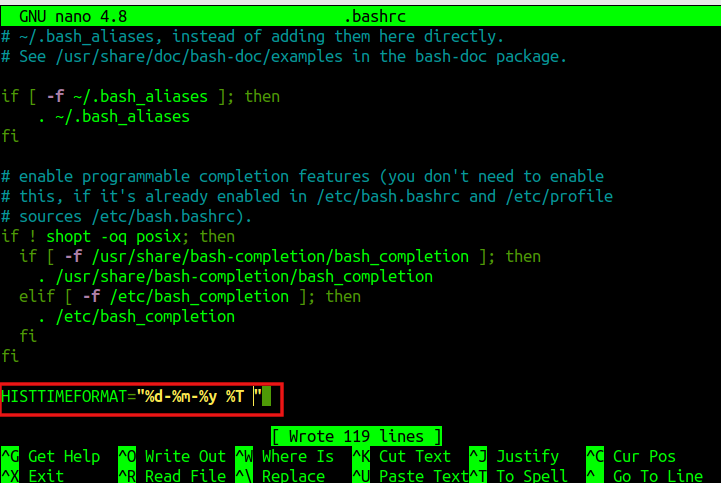
Then, at the end of the file, add the variable:
Save the changes to the .bashrc file.
Then, to use it, type in:
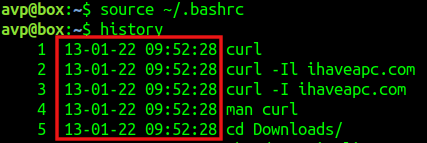
It will now have the timestamp enabled whenever you run the history command from the Terminal. So simply add the way you would want it to be shown by editing the parameters of HISTTIMEFORMAT in the .bashrc file to make it persistent.
All done.